Minerals and vitamins

Minerals and vitamins
On this page, we've gathered everything you need to know about minerals and vitamins.
Our body needs many different vitamins and minerals to function. Here you will find an overview of the most important ones, as well as information about who might need extra supplements.
vitamins and minerals
To begin with, it is important to remember that a healthy and varied Norwegian diet covers much of our need for nutrients. It is also important to know that certain vitamins or minerals in high doses can be harmful.
Most people in Norway need vitamin D supplements
Vitamin D is an important vitamin for the skeleton and our immune system. Many people in Norway have too little of it. This is largely because it is challenging to get enough from diet alone. Between September and April, we don't get any vitamin D from the sun. During the same period, we see a large increase in flu, colds and other viral infections every year. The viruses are around us all year round, but during the winter months our resistance is weakened.
So who might need a vitamin D supplement? The Norwegian Directorate of Health's recommendation to avoid deficiency is 10 mcg daily for infants from 1 week of age and adults up to 75 years of age. From the age of 75, 20 mcg daily is recommended. As with everything else, it is important to remember that there is a difference between doses that avoid deficiency states and doses that take you into the optimal range.
When it comes to vitamin D, there is debate about where the boundary for what is optimal lies. Doctors measure the storage form of vitamin D and not the active form of the vitamin. Excessive levels of the storage form can possibly contribute to inflammation. Other nutrients such as magnesium and boron are important for the conversion from the storage form to the active form of vitamin D. If you take boron and magnesium supplements, you need lower doses of vitamin D supplements due to more efficient conversion and recycling of the vitamin.
Vulnerable groups that may need extra supplements are:
- Adults and children who rarely eat oily fish.
- Older people over 60 years.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women.
- People who eat little.
- People with dark skin color.
Especially during the winter months, supplements may be relevant. If you are unsure whether you need supplements, you can easily get a blood test from your doctor. The optimal range is probably somewhere between 75 and 125 mml/L.
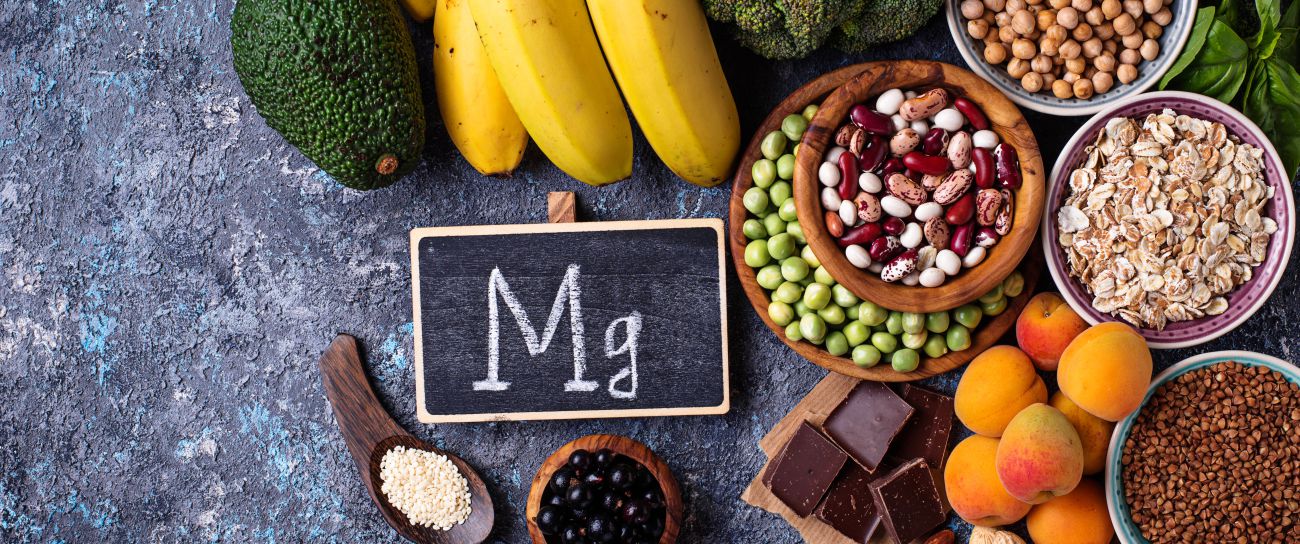
Magnesium
Magnesium (Mg) is a mineral that the body needs to function well. A healthy and varied Norwegian diet usually covers a minimum requirement. Deficiency can occur in connection with some diseases, heavy exercise and the use of diuretic drugs. It is important to note that a minimum requirement to avoid deficiency is not the same as being in the optimal range. It is also worth noting that the magnesium measurements taken at Norwegian doctors' offices are taken in serum and not in whole blood. Magnesium levels in serum are kept very stable by the body. The body would rather drain magnesium from the skeleton than get too low levels of magnesium in serum. Internationally, serum measurements of magnesium are not considered the gold standard. Magnesium measured in red blood cells is.
What does magnesium do in the body?
Magnesium has many important functions in the body. Among other things, the mineral is an important cofactor for several different enzymes, which are involved in the synthesis of proteins, normal cell metabolism and the formation of DNA and RNA. Magnesium is also necessary for the transmission of nerve signals and is particularly important for muscle function in the heart.
Severe magnesium deficiency can also lead to low levels of calcium and potassium. Signs of magnesium deficiency can include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, lethargy and weakness. These are diffuse and vague symptoms that may also have other causes.
Important sources of magnesium
Magnesium cannot be formed in the body and must be supplied via food and drink. Magnesium is found in most foods as the mineral is part of plant chlorophyll. Cereals, fruit and vegetables account for about half of our magnesium intake. The rest comes mainly from dairy products and meat.
How much magnesium do you need daily?
According to Norwegian health authorities, in order to avoid deficiency states:
- Infants: 80 milligrams (mg) of magnesium per day. The need increases with age.
- Adult men and adolescents over 14 years of age: 350 mg per day
- Women, including pregnant and breastfeeding women: 280 mg or more.
Who might need magnesium supplements?
Many people experience improvements in their health challenges when they consume more magnesium. Conditions where you should pay extra attention are wood:
- Lots of training
- Malnutrition
- Prolonged diarrhea
- High age
- Use of diuretic medication
- Alcoholism
Many people experience good effects from magnesium supplements when struggling with cramps.
